
What is a Blood Pressure Chart?
A blood pressure chart is a tool used to track and monitor blood pressure readings over time. It is a visual representation of the two numbers that make up a blood pressure reading: systolic pressure and diastolic pressure. The systolic pressure is the top number, and it represents the pressure in the arteries when the heart beats. The diastolic pressure is the bottom number, and it represents the pressure in the arteries when the heart is at rest between beats.
A blood pressure chart typically displays a range of blood pressure readings, from normal to high. It allows individuals to compare their blood pressure readings to the recommended ranges and identify whether their blood pressure is within a healthy range or if it falls into the high blood pressure category.
Why is a Blood Pressure Chart Important?
A blood pressure chart is an important tool for monitoring and managing blood pressure. It provides valuable information about an individual’s cardiovascular health and can help identify potential risks for heart disease, stroke, and other related conditions.
By regularly tracking blood pressure readings and comparing them to the recommended ranges on a blood pressure chart, individuals can take proactive steps to maintain or improve their cardiovascular health. It can also serve as a guide for healthcare professionals in determining the most appropriate treatment plan for patients with high blood pressure.
How to Use a Blood Pressure Chart
Using a blood pressure chart is simple. Here are the steps to effectively utilize a blood pressure chart:
1. Measure Your Blood Pressure
Begin by measuring your blood pressure using a reliable blood pressure monitor. Make sure you are in a calm and relaxed state before taking the measurement, as stress or physical activity can temporarily elevate blood pressure.
Take note of both your systolic and diastolic pressure readings, as you will need both numbers to interpret your results on the blood pressure chart.
2. Locate Your Blood Pressure Range on the Chart
Once you have your blood pressure readings, find the corresponding range on the blood pressure chart. The chart will typically have color-coded sections or specific ranges indicated for normal, elevated, and high blood pressure.
Identify where your systolic and diastolic blood pressure readings fall within the chart’s ranges.
3. Interpret Your Results
Based on where your blood pressure readings fall on the chart, you can interpret your results:
- If both your systolic and diastolic pressures are within the normal range, congratulations! Your blood pressure is considered healthy.
- If your systolic pressure is elevated, but your diastolic pressure is within the normal range, you may have isolated systolic hypertension.
- If both your systolic and diastolic pressures are elevated, you may have stage 1 or stage 2 hypertension, depending on the severity of the elevation.
- If your blood pressure readings consistently fall within the high blood pressure range, it is essential to consult with your healthcare provider for proper diagnosis and treatment.
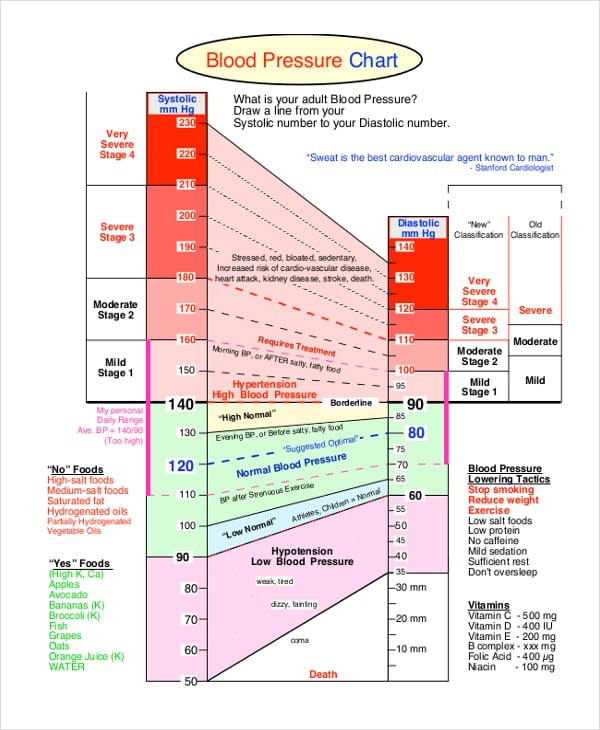

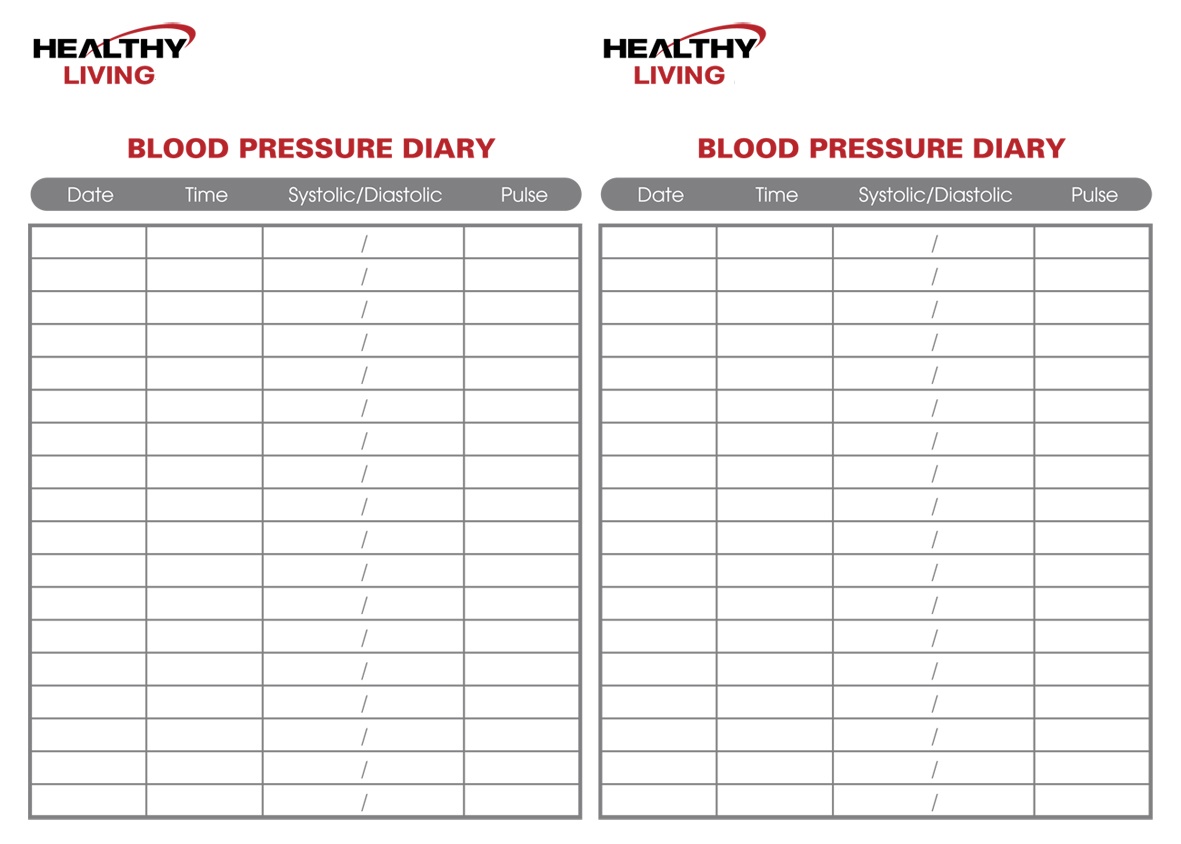
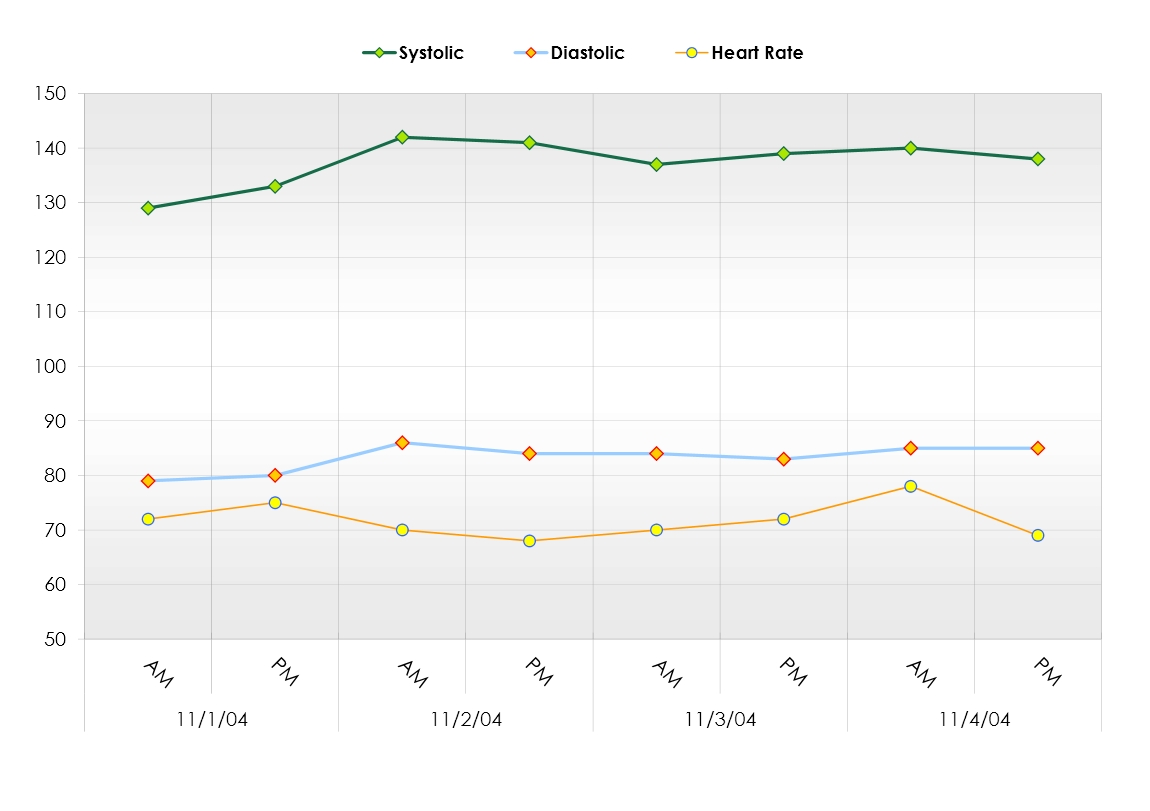
Understanding the Numbers on a Blood Pressure Chart
A blood pressure chart typically includes multiple categories or ranges that indicate different levels of blood pressure. Here is a breakdown of the common categories found on a blood pressure chart:
1. Normal Blood Pressure
Normal blood pressure is considered to be a systolic pressure below 120 mmHg and a diastolic pressure below 80 mmHg. This range indicates a healthy cardiovascular system and a low risk of heart disease.
2. Elevated Blood Pressure
Elevated blood pressure falls between 120-129 mmHg for the systolic pressure and below 80 mmHg for the diastolic pressure. While not classified as high blood pressure, it is a warning sign that individuals are at risk of developing hypertension if preventive measures are not taken.
3. Stage 1 Hypertension
Stage 1 hypertension is characterized by a systolic pressure ranging from 130-139 mmHg or a diastolic pressure ranging from 80-89 mmHg. At this stage, individuals may need to make lifestyle changes or start medication to manage their blood pressure.
4. Stage 2 Hypertension
Stage 2 hypertension involves a systolic pressure of 140 mmHg or higher or a diastolic pressure of 90 mmHg or higher. This stage indicates a more severe form of high blood pressure that often requires medication and significant lifestyle changes to control.
5. Hypertensive Crisis
A hypertensive crisis occurs when the systolic pressure exceeds 180 mmHg and/or the diastolic pressure exceeds 120 mmHg. It is a severe condition that requires immediate medical attention to prevent organ damage or life-threatening complications.
The Importance of Regular Blood Pressure Monitoring
Regular blood pressure monitoring is crucial for individuals of all ages, regardless of whether they have been diagnosed with high blood pressure. Here are some reasons why regular blood pressure monitoring is important:
- Early detection of high blood pressure: Regular monitoring allows individuals to detect high blood pressure early before it causes significant damage to the cardiovascular system.
- Preventive measures: By identifying and monitoring blood pressure trends, individuals can take preventive measures to manage their blood pressure through lifestyle changes such as maintaining a healthy diet, exercising regularly, reducing sodium intake, and managing stress.
- Tracking treatment effectiveness: For individuals already diagnosed with high blood pressure, regular monitoring helps track the effectiveness of treatment plans, including medication and lifestyle modifications.
- Identifying white coat hypertension: Some individuals experience elevated blood pressure readings in a medical setting due to anxiety or stress. Regular monitoring at home can help differentiate between true hypertension and white-coat hypertension.
Tips for Maintaining Healthy Blood Pressure
While some individuals may require medication to manage their blood pressure, many can maintain healthy blood pressure levels through lifestyle modifications. Here are some tips to help maintain healthy blood pressure:
- Follow a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and low-fat dairy products.
- Reduce sodium intake by avoiding processed foods, canned soups, and fast food.
- Engage in regular physical activity, such as brisk walking, cycling, swimming, or jogging.
- Avoid tobacco products and limit alcohol consumption.
- Manage stress through relaxation techniques like deep breathing exercises, meditation, or yoga.
- Maintain a healthy weight by adopting a well-rounded exercise routine and making healthy food choices.
Conclusion
A blood pressure chart is a valuable tool for monitoring and managing blood pressure. By understanding how to interpret the numbers on the chart and regularly monitoring blood pressure, individuals can take proactive steps to maintain or improve their cardiovascular health. Remember, it is always essential to consult with a healthcare professional for proper diagnosis, treatment, and guidance on managing blood pressure.
Blood Pressure Chart Template – Download